Explanation of rser and rser eao Commands in TopSpin
In TopSpin, the rser command is used to read raw time‐domain (FID) data from the ser file of a multi‐dimensional experiment. The eao keyword stands for “echo–antiecho” and instructs TopSpin on how to interpret or separate the raw data when echo–antiecho acquisition has been used in the indirect dimension(s).
rser 1
- Functionality:
Reads the first FID chunk from theserfile “as is.” - Note:
Does not apply the echo–antiecho separation or any special handling for complex data acquired in echo–antiecho mode.
rser eao 1
- Functionality:
Reads the first FID chunk and applies the correct echo–antiecho interpretation for experiments that used echo–antiecho acquisition in the indirect dimension(s). - Processing:
Extracts the real portion of the data if echo–antiecho mode was used—this is typically how you want to view the “first increment” FID in such acquisitions.
When to Use rser eao 1
- Usage Scenario:
Userser eao 1if your experiment was acquired with echo–antiecho in an indirect dimension and you want to view the correctly separated (real) FID for the first increment. - Common Applications:
Frequently applied in 2D/3D experiments (e.g., HSQC, HMQC, triple-resonance protein NMR) where echo/antiecho pulses are used to shift sign, reduce artifacts, or simplify phase cycling. - Example Figure: 4D spectrum recorded using
States-TPPIat all indirect dimensions.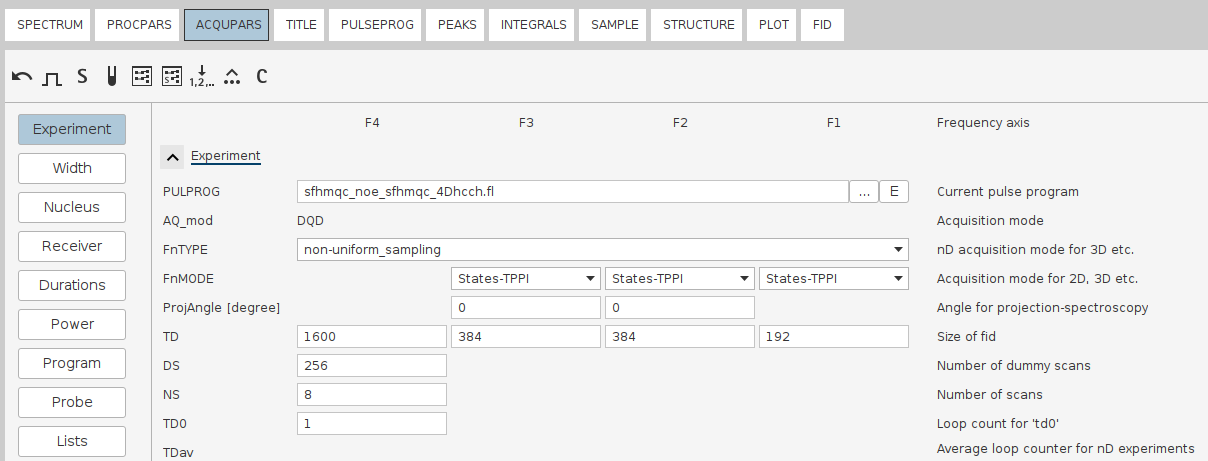
When to Use rser 1
- Usage Scenario:
Userser 1if your experiment was not run with echo–antiecho (for example, TPPI, States, QF, etc.) and you simply need the first time‐domain block of theserfile without any special separation. - Example Figure: 4D spectrum recorded using
Echo-Antiechoat one indirect dimension.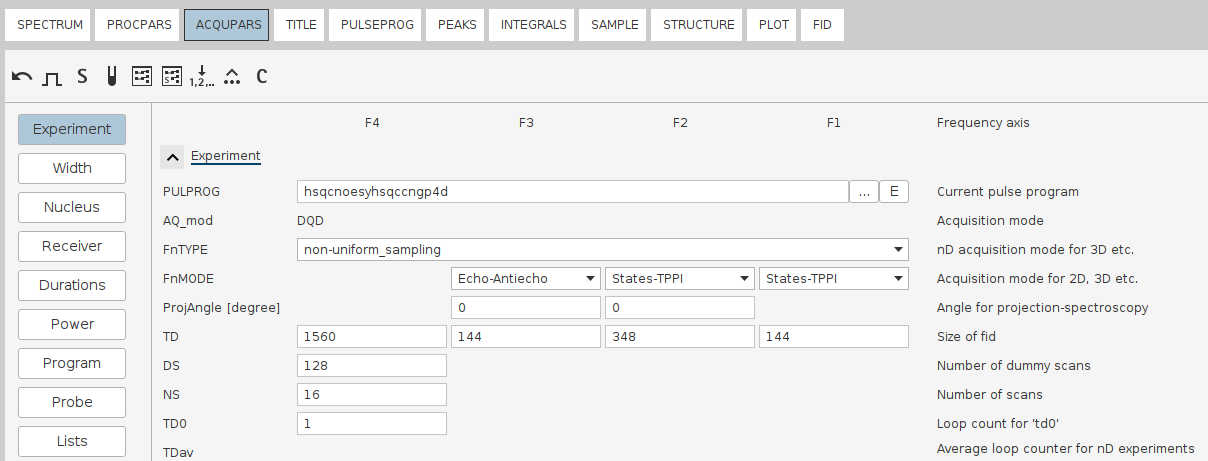
Summary
In short, rser eao is specifically intended for data acquired using an echo–antiecho scheme, ensuring you obtain the correct FID “slice.” Using rser 1 on echo–antiecho data may lead to viewing the raw complex data incorrectly combined, rather than the properly separated FID you expect.